Cloud computing has fundamentally transformed the way we think about and interact with technology. By providing on-demand access to computing resources over the internet, cloud computing allows businesses and individuals to leverage powerful infrastructure, platforms, and software without the need for significant upfront investment. This blog will provide an introduction to cloud computing, explaining its key concepts, deployment models, service models, and benefits.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of various services, such as storage, processing power, and applications, over the internet. Instead of owning and maintaining physical servers and data centers, users can access these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis from cloud service providers (CSPs) like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
Key Concepts
1. On-Demand Self-Service
Users can provision and manage computing resources as needed without human intervention from the service provider. This flexibility allows for quick scaling and efficient use of resources.
2. Broad Network Access
Cloud services are accessible over the internet from a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktops. This ensures that users can access their applications and data from anywhere at any time.
3. Resource Pooling
Cloud providers use a multi-tenant model to serve multiple customers with a pool of shared resources, dynamically allocating and reallocating resources based on demand. This optimizes efficiency and reduces costs.
4. Rapid Elasticity
Cloud resources can be quickly scaled up or down to match demand. This elasticity is particularly beneficial for handling varying workloads and ensures that users only pay for what they use.
5. Measured Service
Cloud systems automatically control and optimize resource use by leveraging metering capabilities. Users are billed based on their usage of services, providing transparency and cost control.
Deployment Models
1. Public Cloud
In the public cloud model, services are delivered over the public internet and shared across multiple organizations. Public clouds are ideal for applications with varying workloads and those requiring quick deployment. Examples include AWS, Azure, and GCP.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, providing greater control over data, security, and compliance. Private clouds can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. They are suitable for organizations with stringent regulatory requirements or specific performance needs.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud model combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. This approach offers greater flexibility and optimizes existing infrastructure, providing a balanced approach to scalability, security, and cost-efficiency.
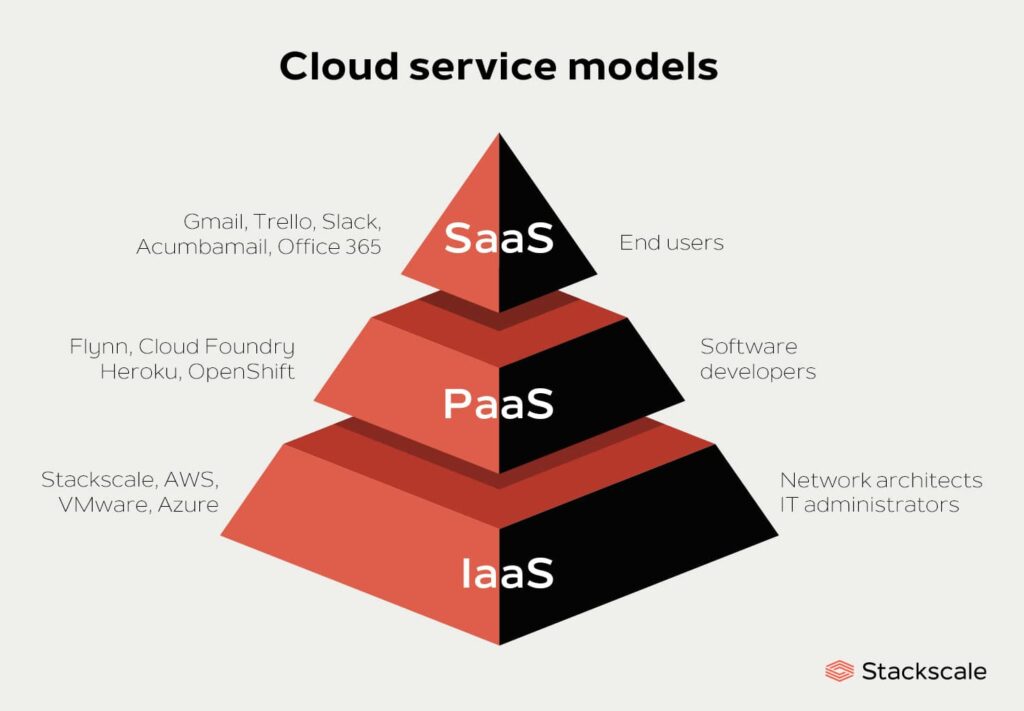
Service Models
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networks. Users can rent these resources on-demand and scale them as needed. Examples include AWS EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS includes services like application hosting, databases, and development tools. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure App Service, and Google App Engine.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access these applications via a web browser without needing to install or maintain them locally. Examples include Google Workspace, Microsoft Office 365, and Salesforce.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cost Savings: Cloud computing eliminates the capital expense of buying hardware and software, as well as setting up and running on-site data centers.
Scalability: Cloud services can be scaled up or down to accommodate changing demands, providing flexibility and optimizing resource use.
Performance: Major cloud providers offer high-performance infrastructure with global networks, ensuring low latency and high availability.
Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures, including data encryption, access control, and regular security updates, to protect user data.
Disaster Recovery: Cloud computing offers robust disaster recovery solutions, ensuring business continuity and data protection in case of unforeseen events.
Collaboration: Cloud-based tools and applications facilitate collaboration by allowing multiple users to work on the same documents and projects from different locations.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its numerous benefits, cloud computing also faces challenges, such as data privacy concerns, vendor lock-in, and regulatory compliance. As the technology continues to evolve, innovations like edge computing, serverless architectures, and AI-driven cloud services are expected to further enhance cloud computing capabilities and address these challenges.
Conclusion
Cloud computing represents a paradigm shift in how we access and utilize computing resources. By offering on-demand, scalable, and cost-effective solutions, cloud computing enables businesses and individuals to innovate and operate more efficiently. As the technology advances, it will continue to drive digital transformation across various industries, shaping the future of IT infrastructure and service delivery.

